DocsEmissary-ingress
3.1
Consul integration
Consul integration
Contents
Consul is a widely used service mesh. Emissary-ingress natively supports service discovery and unauthenticated communication to services in Consul. Additionally, the Ambassador Consul Connector enables Emissary-ingress to encrypt and authenticate its communication via mTLS with services in Consul that make use of Consul's Connect feature.
Architecture overview
Using Consul with Emissary-ingress is particularly useful when deploying Emissary-ingress in hybrid cloud environments where you deploy applications on VMs and Kubernetes. In this environment, Consul enables Emissary-ingress to securely route over TLS to any application regardless of where it is deployed.
In this architecture, Consul serves as the source of truth for your entire data center, tracking available endpoints, service configuration, and secrets for TLS encryption. New applications and services automatically register themselves with Consul using the Consul agent or API. When you send a request through Emissary-ingress, Emissary-ingress sends the request to an endpoint based on the data in Consul.
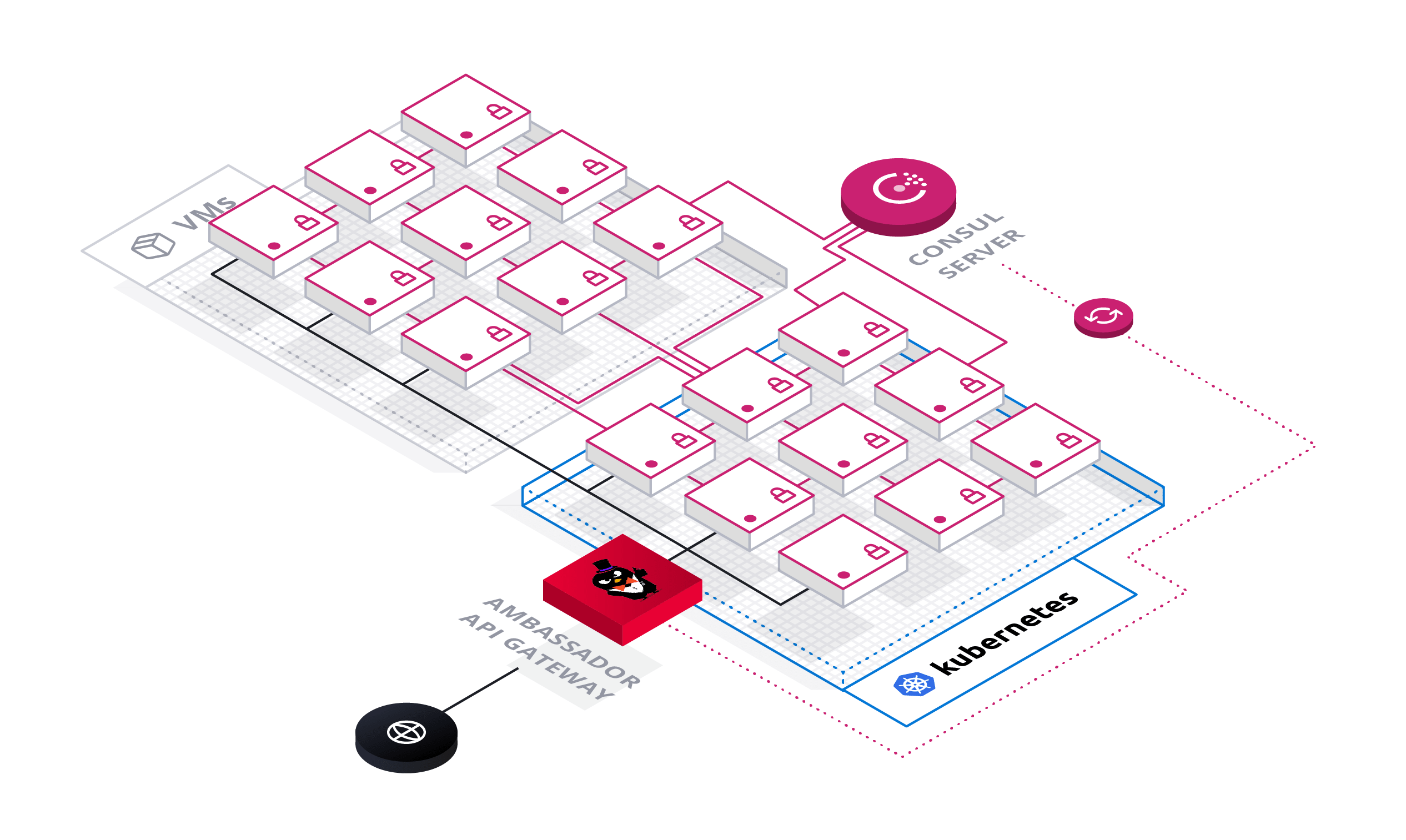
This guide first instructs you on registering a service with Consul and using Emissary-ingress to dynamically route requests to that service based on Consul's service discovery data, and subsequently instructs you on using using the Ambassador Consul Connector to use Consul for authorizing and encrypting requests.
Installing Consul
If you already have Consul installed in your cluster, then go ahead and skip to the next section.
Before you install Consul, make sure to check the Consul documentation for any setup steps specific to your platform. Below you can find setup guides for some of the more popular Kubernetes platforms. This step is primarily to ensure you have the proper permissions to set up Consul. You can skip these guides if your cluster is already configured to grant you the necessary permissions.
- Microsoft Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Add the Hashicorp repository for installing Consul with Helm. If you do not have Helm installed, you can find an installation guide here.
Create a new
consul-values.yamlYAML file for the Consul installation values and copy the values below into that file.Install Consul with Helm using the
consul-values.yamlvalues file you just created.
Installing Emissary-ingress
If you have not already installed Emissary-ingress in to your cluster, then go to the quick start guide before continuing any further in this guide.
Using Consul for service discovery
This section of the guide instructs you on configuring Emissary-ingress to look for services registered to Consul, registering a demo application with Consul, and configuring Emissary-ingress to route to this application using endpoint data from Consul.
In this tutorial, you deploy the application in Kubernetes. However, this application can be deployed anywhere in your data center, such as on a VM.
Configure Emissary-ingress to look for services registered to Consul by creating the
ConsulResolver. Usekubectlto apply the following manifest:This tells Emissary-ingress that Consul is a service discovery endpoint.
You must set the resolver to your
ConsulResolveron a per-Mappingbasis, otherwise for thatMappingEmissary-ingress uses the default resolver. That is, in order for aMappingto make use of a service registered in Consul, you need to addresolver: consul-dc1to thatMapping.For more information about resolver configuration, see the resolver reference documentation. (If you're using Consul deployed elsewhere in your data center, make sure the
addresspoints to your Consul FQDN or IP address).Deploy the Quote demo application. Use
kubectlto apply the following manifest:The Quote application contains code to automatically register itself with Consul, using the
CONSUL_IPandPOD_IPenvironment variables specified within thequote-consulcontainer spec.When you apply this manifest, it registers the
Podin thequote-consulDeploymentas a Consul service with the namequote-consuland the IP address of thePod.Verify the
quote-consulDeployment'sPodhas been registered with Consul. You can verify this by accessing the Consul UI.First use
kubectl port-forwardto make the UI available on your local workstation:Then, while the port-forward is running, go to http://localhost:8500/ in a web browser. You should see a service named
quote-consul.After you have verified that you see the
quote-consulservice in your web browser, you may kill the port-forward.Configure Emissary-ingress to make use of this
quote-consulservice. Usekubectlto apply the following manifest:Note that in the above config:
servicerefers to the service name you specified in thequote-consulDeployment.resolvermust be set to theConsulResolverthat you created in the previous step.load_balancermust be set to configure Emissary-ingress to route directly to the Quote application endpoints that are retrieved from Consul.
Send a request to the
/quote-consul/API endpoint in order to validate that Emissary-ingress is now making use of that service:
Using Consul for authorization and encryption
In this part of the guide, you'll install a different version of the demo application that now uses Consul's Connect feature to authorize its incoming connections using mTLS, and install Ambassador Consul Connector to enable Emissary-ingress to authenticate to such services.
The following steps assume you've already set up Consul for service discovery, as detailed above.
The Ambassador Consul Connector retrieves the TLS certificate issued by the Consul CA and stores it in a Kubernetes
Secretfor Emissary-ingress to use. Deploy the Ambassador Consul Connector withkubectl:This installs in to your cluster:
- RBAC resources.
- The Ambassador Consul Connector service.
- A
TLSContextnamedambassador-consulto load theambassador-consul-connectSecretinto Emissary-ingress.
Deploy a new version of the demo application, and configure it to inject the Consul Connect sidecar by setting
"consul.hashicorp.com/connect-inject"totrue. Note that in this version of the configuration, you do not have to configure environment variables for the location of the Consul server. Usekubectlto apply the following manifest:This deploys a demo application
Deploymentcalledquote-connect(different than thequote-consulDeploymentin the previous section) with the Consul Connect sidecar proxy. The Connect sidecar registers the application with Consul, requires TLS to access the application, and exposes other Consul Service Segmentation features.The annotation
consul.hashicorp.com/connect-injectbeing set totruein thisDeploymenttells Consul that you want thisDeploymentto use the Consul Connect sidecar. The sidecar proxies requests to the service that it is attached to. Keep this in mind mind when debug requests to the service.Verify the
quote-connectDeployment'sPodhas been registered with Consul. You can verify this by accessing the Consul UI.First use
kubectl port-forwardto make the UI available on your local workstation:Then, while the port-forward is running, open http://localhost:8500/ in a web browser. You should see a service named
quote-connect.After you have verified that you see the
quote-connectservice in your web browser, you may kill the port-forward.Create a
Mappingto configure Emissary-ingress route to thequote-connectservice in Consul. Usekubectlto apply the following manifest:Note that in the above config:
servicemust be set to the name of the Consul sidecar service. You can view this withkubectl get svc -Ait should follow the format of{service name}-sidecar-proxy.resolvermust be set to theConsulResolvercreated when configuring Emissary-ingress.tlsmust be set to the TLSContext storing the Consul mTLS certificates, which isambassador-consulin the standardambassador-consul-connector.yaml.load_balancermust be set to configure Emissary-ingress to route directly to the application endpoints that are retrieved from Consul.
When you apply this manifest, it creates a Mapping that routes to the
quote-connectservice in Consul.Send a request to the
/quote-connect/API endpoint in order to validate that Emissary-ingress is now using mTLS to encrypt and authenticate communication with that service:
Environment variables
The Ambassador Consul Connector can be configured with the following environment variables. The defaults are best for most use-cases.
| Environment Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
_AMBASSADOR_ID | Set the Ambassador ID so multiple instances of this integration can run per-Cluster when there are multiple Emissary-ingresses (Required if AMBASSADOR_ID is set in your Emissary-ingress Deployment) | "" |
_CONSUL_HOST | Set the IP or DNS name of the target Consul HTTP API server | 127.0.0.1 |
_CONSUL_PORT | Set the port number of the target Consul HTTP API server | 8500 |
_AMBASSADOR_TLS_SECRET_NAME | Set the name of the Kubernetes v1.Secret created by this program that contains the Consul-generated TLS certificate. | $AMBASSADOR_ID-consul-connect |
_AMBASSADOR_TLS_SECRET_NAMESPACE | Set the namespace of the Kubernetes v1.Secret created by this program. | (same Namespace as the Pod running this integration) |
More information
For more about Emissary-ingress's integration with Consul, read the service discovery configuration documentation.








